kar7mp5
[Python] Implementation of Differences (SSD) through Depth Map Sum of Squared 본문
AI/Vision
[Python] Implementation of Differences (SSD) through Depth Map Sum of Squared
kar7mp5 2024. 12. 9. 22:58728x90
௹ 양안 시차 (Binocular Disparity)
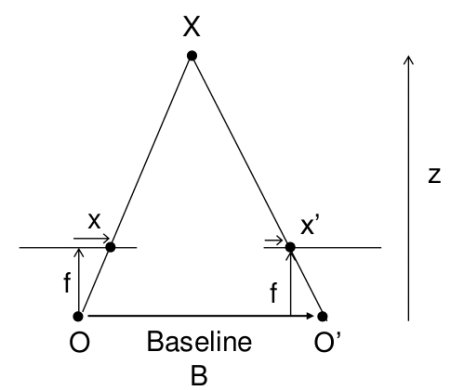
이미지 출처: OpenCV official docs
양안 시차는 인간과 같은 양안 시각 시스템에서 두 눈이 약간 다른 각도에서 대상을 보는 데서 발생하는 시각적 차이를 의미한다.
가까운 사물일 수록 시차(Disparity)가 크고, 멀리에 있는 사물일 수록 시차가 작다.
$$
disparity = x - x^\prime = \frac{Bf}{Z}
$$
$x$와 $x^\prime$: 3D 공간 상의 한 점(Scene Point)이 두 카메라에서 투영된 이미지 평면 상의 좌표
$B$: 두 카메라 센터 간의 거리 (Baseline)
$f$: 카메라의 초점 거리(Focal Length)
깊이(Depth): 3D 공간 상의 한 점(Scene Point)에서 카메라까지의 거리
௹ The Sum of Squared Differences (제곱 차 합)
기본 개념으로 왼쪽, 오른쪽 이미지가 유사하지 않을 수록 거리가 가깝고, 유사할 수록 거리가 멀다고 설명했다.
여기서 핵심은 "두 이미지 간 유사도" 라고 볼 수 있다.
필자는 이번에 MSE(평균제곱오차) 방식으로 유사도를 구하였다.
$$
SSD(x, y, d) = \sum_{i=-\frac{B}{2}}^{\frac{B}{2}} \sum_{j=-\frac{B}{2}}^{\frac{B}{2}} \left( I_L(x + i, y + j) - I_R(x + i - d, y + j) \right)^2
$$
$I_L$: 왼쪽 이미지
$I_R$: 오른쪽 이미지
$B$: Block size(블록 사이즈); 비교할 이미지 크기
$d$: Disparity(깊이)
OpenCV로 구현
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import cv2
# Load images
imgL = cv2.imread('./data/tsukuba_l.png',0)
imgR = cv2.imread('./data/tsukuba_r.png',0)
# Compute disparity
stereo = cv2.StereoBM_create(numDisparities=16, blockSize=15)
disparity = stereo.compute(imgL,imgR)
# Display the plots
plt.imshow(disparity,'inferno')
plt.show()
Numpy로 구현
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def compute_disparity(imgL, imgR, num_disparities, block_size):
"""
Computes the disparity map between a pair of rectified stereo images.
Args:
imgL (np.ndarray): Left grayscale image.
imgR (np.ndarray): Right grayscale image.
num_disparities (int): Maximum disparity range to search.
block_size (int): Size of the square block for block matching.
Returns:
np.ndarray: Disparity map with the same dimensions as the input images.
"""
# Ensure the images are numpy arrays and have float32 type
imgL = np.asarray(imgL, dtype=np.float32)
imgR = np.asarray(imgR, dtype=np.float32)
# Get the dimensions of the images
height, width = imgL.shape
# Initialize the disparity map with zeros
disparity_map = np.zeros((height, width), dtype=np.float32)
# Calculate half of the block size for easier indexing
half_block = block_size // 2
# Loop over each pixel in the left image
for y in range(half_block, height - half_block):
for x in range(half_block, width - half_block):
# Define the block region in the left image
blockL = imgL[y - half_block:y + half_block + 1, x - half_block:x + half_block + 1]
# Initialize variables for the best match
min_ssd = float('inf')
best_disparity = 0
# Search for the best disparity in the range [0, num_disparities)
for d in range(num_disparities):
if x - d - half_block < 0:
continue
# Define the block region in the right image
blockR = imgR[y - half_block:y + half_block + 1, x - d - half_block:x - d + half_block + 1]
# Compute the sum of squared differences (SSD) between blocks
ssd = np.sum((blockL - blockR) ** 2)
# Update the best disparity if SSD is smaller
if ssd < min_ssd:
min_ssd = ssd
best_disparity = d
# Assign the best disparity value to the disparity map
disparity_map[y, x] = best_disparity
return disparity_map
# Load grayscale images as numpy arrays
imgL = plt.imread('./data/tsukuba_l.png')
imgR = plt.imread('./data/tsukuba_r.png')
# Ensure the images are 2D arrays (grayscale)
if imgL.ndim == 3:
imgL = imgL[:, :, 0] # Convert to grayscale if needed
if imgR.ndim == 3:
imgR = imgR[:, :, 0] # Convert to grayscale if needed
# Parameters for disparity computation
num_disparities = 16
block_size = 20
# Compute the disparity map
disparity = compute_disparity(imgL, imgR, num_disparities, block_size)
# Visualization of the results
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 3))
# Original image
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(imgL, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Original Image')
plt.axis("off")
# Disparity map
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(disparity, cmap='inferno')
plt.colorbar()
plt.title('Disparity Map')
plt.axis("off")
# Display the plots
plt.show()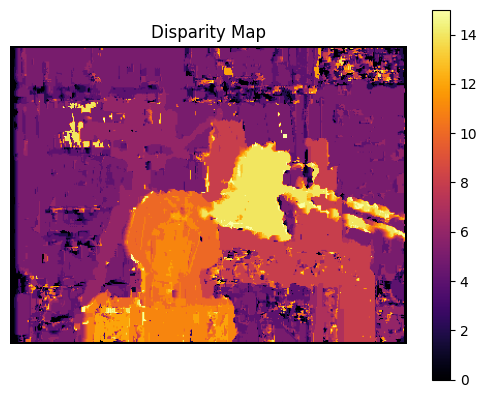
728x90
